Endoscopic Ultrasonography - EUS (Part Two)
What is the preparation for endoscopic ultrasound?
The doctor needs to be informed about your health condition, especially if you have any medication allergies or if you have other diseases such as; heart, lungs, diabetes, etc. You also need to inform the doctor if you are allergic to iodine or shellfish because iodine-containing contrast might be used during the procedure.
If aspiration with a needle is to be done, your blood will need to be examined to exclude the possibility of clots (blood clotting). It is very important that you inform the doctor if you have a family history of hemorrhage or if you are taking blood-thinning medications (such as aspirin, plavix, sintrom, etc)
It is very important that you inform the doctor about any kind of medication you are taking, including herbal medicines.
Taking antibiotics usually does not need to be stopped.
The endoscopic ultrasound will be performed under sedation (venous sleep) so you will not be able to work or drive for 24 hours. This means you will need to be accompanied by a family member.
You will need to have an empty stomach for more than 6 hours without eating. In cases where the endoscopic ultrasound will be rectal, you will need to use a laxative that will be prescribed and instructions will be given by the doctor on how to use it.
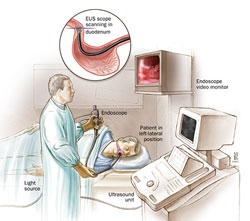
How is the endoscopic ultrasound performed?
Once you arrive at the endoscopic center, the nurse or doctor will explain the procedure to you and will answer all the questions you may have. You will also be asked to sign a consent form.
After this, your preparation for the procedure will begin. A venous catheter will be placed for sedation (venous sleep) and to administer venous fluids and medications.
You will also be monitored for vital signs; blood pressure, blood oxygenation, and pulse.
Immediately after you fall asleep, the procedure will begin using a special endoscope that will be inserted through the mouth or rectum (as needed).
Due to sedation, you will not feel pain but you might experience a slight discomfort.
The doctor will carefully observe your digestive tract on a TV monitor and the ultrasound images on another monitor.
The procedure can last about 30-90 minutes depending on the need for other procedures such as: (FNA) needle aspiration.
After the procedure, you will be ready to walk and eat after 2 hours.
Once the effects of the sedation have worn off, the doctor will explain the results to you. Later, you are free to leave accompanied by a family member.
Light meals and fluids are allowed the day after the examination. You may experience mild abdominal bloating due to the examination, but don’t worry as it passes quickly
You may feel mild throat pain which can pass after using saltwater gargles. You should immediately contact the doctor or present to the health center if you have: severe pain, clear vomiting or with blood content, fever, and temperature.
What are the risks of endoscopic EUS?
Like any other endoscopic procedure, EUS is safe and tolerated by patients. However, there is no procedure without its own risks, but EUS has them very rarely. The possibility of complications from EUS without the needle aspiration procedure is 1/2000. Sometimes patients may have signs of a reaction such as itching and red skin spots or vomiting from the medications used during the procedure.
Also, a swelling (like a lump) at the site where the catheter was placed can occur, a situation that is not problematic and resolves over time. If it does not disappear within a certain period, you should consult with the doctor.
The main complication of EUS is perforation (tearing of the intestinal or stomach wall) a situation that may require surgery. However, this complication is very rare and necessary precautions are taken during the procedure to avoid it.
When the needle aspiration procedure is performed, the chances of complications occurring are higher but still very rare, with a percentage of 0.5-1.0 Passing the needle through the walls may cause minor hemorrhage. If the hemorrhage continues, the patient is hospitalized for a short period for observation and the need for a blood transfusion is very rare.
Infection is another complication from the needle aspiration procedure, which can occur during the aspiration (suction) of cyst fluids, and antibiotic therapy is given after the procedure. If the needle aspiration is done on the pancreas, pancreatitis (infection of the pancreas) can occur very rarely. Pancreatitis is a situation that requires the patient's hospitalization, observation, bed rest, administration of fluids, and venous medications. Usually, this situation resolves spontaneously within a few days.